Scoliosis Treatment
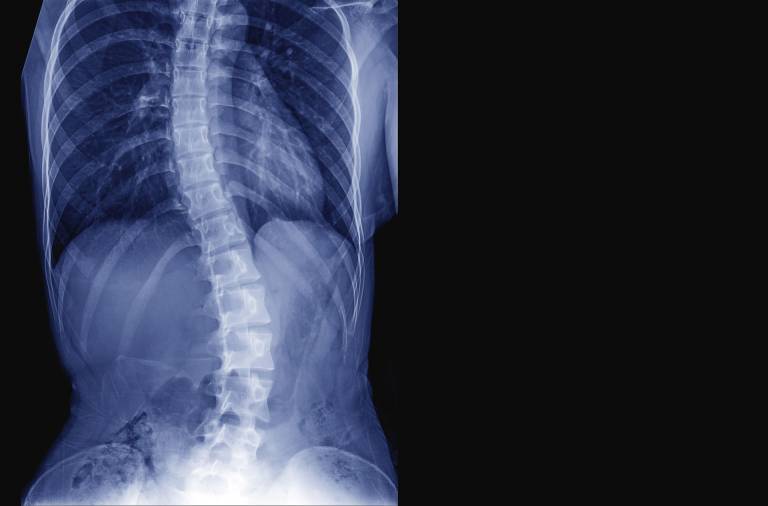
Scoliosis, an abnormal spine curvature, challenges one’s physical well-being. In severe scoliosis, the limitations on an individual’s range of motion and flexibility can significantly impact active engagement in sports, exercise, and other physical activities, influencing overall quality of life.
However, amidst these challenges, there is hope. Scoliosis treatment can improve the condition and enhance physical well-being.
What is scoliosis?
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterised by an abnormal spine curvature, presenting as a sideways or lateral deviation from the normal straight alignment. This curvature can manifest in various forms and degrees, impacting the overall structure of the spine.
Unlike the spine’s natural curves, scoliosis presents an additional lateral curve.
What are the symptoms of scoliosis?
Scoliosis often develops gradually, and in its early stages, it may not cause noticeable symptoms. However, as the curvature progresses, individuals may experience the following symptoms.
Uneven shoulders
Uneven hips
Uneven shoulder blades
Visible curve of the spine
Back pain or discomfort
Fatigue
What causes scoliosis?
Genetic predisposition
Some individuals with a family history of spinal deformities are genetically predisposed to scoliosis. Specific genetic factors may influence the development of scoliosis, contributing to the abnormal curvature of the spine.
Neuromuscular conditions
Individuals with cerebral palsy, a group of neurological disorders affecting movement and coordination, may develop scoliosis due to muscle imbalances and weakness.
Inherited muscle-wasting conditions like muscular dystrophy can also lead to scoliosis, as muscle weakness affects the spine’s ability to maintain proper alignment.
Congenital abnormalities
Congenital scoliosis occurs when the spine develops with irregularities, such as malformed or fused vertebrae, during fetal growth.
Spinal cord abnormalities affect the spinal cord’s development and can contribute to scoliosis. Anomalies in the nervous system may lead to muscle imbalances and curvature.
Idiopathic causes
The majority of scoliosis cases fall under the category of idiopathic, meaning the exact cause is unknown.
Degenerative factors
Degenerative scoliosis is associated with ageing and the gradual breakdown of spinal discs and joints, leading to curvature.
Weakening bones due to conditions like osteoporosis can contribute to scoliosis, especially in the elderly.
How is scoliosis diagnosed?
Diagnosing scoliosis involves a comprehensive assessment, combining clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Early detection is crucial for effective management, making routine screenings vital, especially during adolescence. Here’s a breakdown of the diagnostic process for scoliosis.
Clinical evaluation
Physical assessment
- The healthcare provider observes the individual’s posture, alignment, and symmetry.
- Shoulder heights, hip levels, and noticeable curves or asymmetries are carefully assessed.
Adam’s forward bend test
- During this test, the individual is asked to bend forward at the waist, allowing the healthcare provider to observe any spinal asymmetry or curvature.
Imaging studies
X-rays
- X-rays are a primary tool for diagnosing scoliosis and assessing the curvature’s severity.
- They provide detailed spine images in both frontal and lateral views, enabling measurement of the curve’s angle (Cobb angle).
MRI or CT scans
- In cases where additional details are needed, such as identifying the cause or assessing spinal cord involvement, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be recommended.
What are the types of scoliosis?
Congenital scoliosis
Congenital scoliosis occurs at birth and results from abnormal vertebral development during fetal growth.
Idiopathic scoliosis
Idiopathic scoliosis is the most common type and usually develops during adolescence. The cause is unknown, making early detection and monitoring critical for effective treatment.
Neuromuscular scoliosis
Neuromuscular scoliosis is associated with underlying neuromuscular conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy.
Degenerative scoliosis
Degenerative scoliosis occurs later in life and is often linked to ageing, as the spine undergoes wear and tear over time.
What are the treatment options for scoliosis?
With its diverse presentations and causes, scoliosis demands a tailored approach to spinal scoliosis treatment. The strategies can be broadly categorised into non-surgical and surgical treatments, each serving a specific purpose in managing the condition.
Non-surgical treatment
Observation and monitoring
For mild cases or cases with a low risk of progression, healthcare professionals may recommend periodic monitoring through physical examinations and X-rays.
Physical therapy
Targeted exercises and stretches are designed to improve muscle strength, flexibility, and overall spinal function. Physical therapy is often recommended for both adolescents and adults with scoliosis.
Bracing
Braces are custom-made to provide external support and prevent further curvature progression, particularly in growing adolescents. The type of brace and duration of use depends on factors like age, skeletal maturity, and the severity of scoliosis.
Pain management
Pain associated with scoliosis can be managed through medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. Pain management strategies are essential to enhance the individual’s quality of life.
Surgical treatment
Spinal fusion
Spinal fusion involves the surgical fusion of vertebrae to correct the curvature. Metal rods, screws, or other devices may be used to stabilise the spine during the fusion process.
Instrumentation
Various instrumentation techniques, such as hooks, wires, or screws, are employed to support the spine and maintain correction during and after surgery.
Vertebral body tethering
This method involves attaching a flexible cord to the spine, allowing controlled movement while guiding the growth of the spine. It is often considered for some instances in adolescents.
Osteotomy
Osteotomy involves removing or reshaping parts of the spine to improve alignment. This technique is typically reserved for severe cases and requires careful planning.
What symptoms may indicate the need for scoliosis surgery?
Scoliosis surgery becomes a consideration when the condition progresses to a point where non-surgical interventions no longer effectively manage symptoms, and there is a risk of further complications. Here are signs and scenarios that may indicate the need for scoliosis surgery.
Severe curvature
Progression of curvature
Pain and discomfort
Breathing difficulties
Impaired functionality
How long is the recovery period after a spinal surgery for scoliosis?
The recovery period after spinal surgery for scoliosis is a crucial phase that varies based on the type of surgery, individual health factors, and the extent of the procedure. Generally, individuals may need several weeks to months for initial recovery, followed by a more extended period of rehabilitation and physical therapy.
What is the cost of scoliosis surgery in Singapore?
The cost of scoliosis surgery can vary according to the severity of the condition, the type of surgery needed, and post-operative care, contributing to the overall expenses.
In Singapore, the costs may also depend on the specific medical facility chosen for the procedure.
Scoliosis treatment in Singapore
Timely detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes, offering a path to a healthier and more comfortable life. If you have scoliosis concerns, consult a spine specialist in Singapore for personalised advice and guidance tailored to your unique situation.
At Achieve Orthopaedic and Spine Centre, our dedicated team of orthopaedic and spine specialists is committed to providing comprehensive and personalised care for individuals with scoliosis. Our approach integrates medical expertise and a patient-centred focus to ensure effective spinal scoliosis treatment outcomes.
To learn more about scoliosis treatment, book a consultation with us.

Wu Pang Hung
ABOUT AUTHOR
Dr. Wu Pang Hung is an experienced orthopaedic and spine surgeon in Singapore, specialising in both uniportal and biportal endoscopic spine procedures for complex cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spinal conditions. With over 10 years in the field, he is actively involved in numerous spine societies and contributes to several international journals and textbooks. Dr. Wu has also received specialised training in spine surgery across Canada, South Korea, Japan, and Germany.
Contact Us
WHATSAPP US @+65 9746 6178
CALL US @+65 9746 6178
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Scoliosis often develops during adolescence, between the ages of 10 and 15, but can occur at any age.
The severity is usually determined by measuring the degree of curvature on X-rays.
Bracing is frequently indicated for moderate curvature, and its success varies according to factors such as compliance and case specificity.
Exercises focusing on strengthening the core muscles and improving flexibility can be beneficial.
While physical therapy can help manage symptoms and improve function, it may not correct the curvature entirely.
Success rates vary, but surgery can significantly reduce the curvature and improve quality of life.
We generally recommend monitoring and follow-up visits every four to six months for adolescents and growing children.
Adults with mild scoliosis may require less frequent monitoring, with check-ups typically scheduled on an annual basis. Meanwhile, individuals with moderate to severe scoliosis may benefit from more frequent follow-up appointments every six months or more frequently.
Regular monitoring is essential to track the development of the condition, with follow-up appointments scheduled based on the treatment plan.
While scoliosis may not cause complications, severe curvature may lead to serious issues such as back pain or respiratory problems.
The impact varies, but scoliosis can affect mobility, posture, and, in severe cases, overall quality of life.
In some cases, scoliosis may progress, especially if left untreated. Regular monitoring is essential for early intervention.
Individuals with scoliosis should be cautious with activities that strain the spine and seek guidance from healthcare professionals regarding lifestyle adjustments.
